Fatty Liver Disease – The Scourge of the Trucking Industry
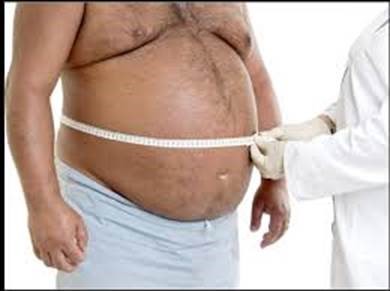
Fatty Liver is the scourge of the trucking industry. Several years ago, Dave Nemo and I had the head of the Fatty Liver Clinic at Duke University School of Medicine on Dave’s program. We found out some very interesting information. Like what causes fatty liver? Well, it is self-induced and is what you eat and keep on eating. The picture above is the most visible symptom of fatty liver disease; a large distended belly. While many people will have no outward symptoms, other outward indications are flabby leg, spider-like blood vessels, yellowing of the skin, and eyes, and swelling of the legs and abdomen. Subjectively, the most common symptoms are fatigue, weakness, weight loss, loss of appetite, nausea, and itching, continual sleepiness and drowsiness. Sleep apnea is the gas on the fire and, if OSA is untreated, fatty liver progress to its side-kick Metabolic syndrome. The latter syndrome, sometimes called syndrome X, will make your life unlivable. Metabolic syndrome leads to serious sleep apnea which, if untreated, is the gasoline that feeds the fire. Fatty Liver disease includes two types, Alcoholic Liver (ALD) and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFLD). Most truckers are not alcoholics so we are looking at NAFLD.
NAFLD is associated with insulin resistance and often referred to as the hepatic piece of the puzzle of metabolic syndrome. This leads to an increase in cardiovascular deaths as well. In addition, the process can progress or change to Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) which causes an inflammatory hepatitis. This hepatitis progress to cirrhosis and fibrosis (scar tissue), and can be a pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver. This leads to possible transplant and eventual post-transplant death.
Total cost to the U.S. is $290 billion annually according to the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Published in the Internal Medicine News.
These conditions and the statistics below demonstrate the magnitude of this problem and its potential impact on trucking.
Fatty Liver Disease Facts and Stats
- Fatty liver affects up to 25% of the American population
- In the United States, it is the most common form of chronic liver disease, affecting an estimated 80 to 100 million people.
- Most liver fat comes from fatty acid in the blood-26% of liver fat is formed in a process called de novo lipogenesis
- 16,000 are on the transplant list – 6,000 are performed each year
- Liver is considered fatty if more than 5% is fat
Two Types of Fatty Liver Disease
- Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) – You can get from drinking too much alcohol – It can even show up after short periods of binge drinking. Genetics can also play a role on whether you get ADL or not. They can affect the chances that you become an alcoholic and how you break down alcohol.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFLD) – It’s not clear what causes NAFLD liver disease, but it tends to run in families.
Risk Factors for Fatty Liver Disease
- Middle Age
- Over weight
- Obese-excess belly fat
- High Cholesterol
- Diabetes-insulin resistance
- Sugary beverage consumptions
- Viral Hepatitis
- Fast Weight Loss
- Malnutrition
Medication for Fatty Liver Disease
- Aspirin
- Acetaminophen
- Ibuprofen
- Naproxen
- Dilantin, tetracycline
- Diflucan
- Tegretol
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
- Feeling tired
- Loss of Weight
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Confusion
- Poor Judgement or Trouble Concentrating
- Pain in the center or right upper part of your belly
- Skin on your neck or under your arms may have dark colors of patches
- If you have ALD, you will notice worsening of the symptoms after periods of heavy drinking
- If you have cirrhosis- scarring of the liver – your symptoms may also include:
- Fluid retention
- Wasting of muscles
- Jaundice
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
- Blood Tests
- Coagulation panel (prothrombin time(PT), INR
- Albumin level
- Bilirubin
- Platelet count
- Glucose
- GGT (Gamma-glutamyl trans peptidase)
- ALP (alkaline phosphatase)
- LD or LDH
- Ultra Sound
- MRI/Cat Scan
- Biopsy of the liver
Treatment for Fatty Liver Disease
- If ALD – stop drinking
- If NAFLD- weight loss, best foods to consume
- protein
- high dietary fiber and whole wheat grains
- vegetable
- citrus fruits
Look for another article on Fatty Liver Disease/Treatment. If you would like to talk to me about Fatty Liver Disease please contact me through the Dr. John’s Medical Solutions website (www.expressms.net) or at the call center number (800) 855-1356.
